Table of Contents
Benefits of Steel Structure Box Houses in Green Building Evaluation Systems
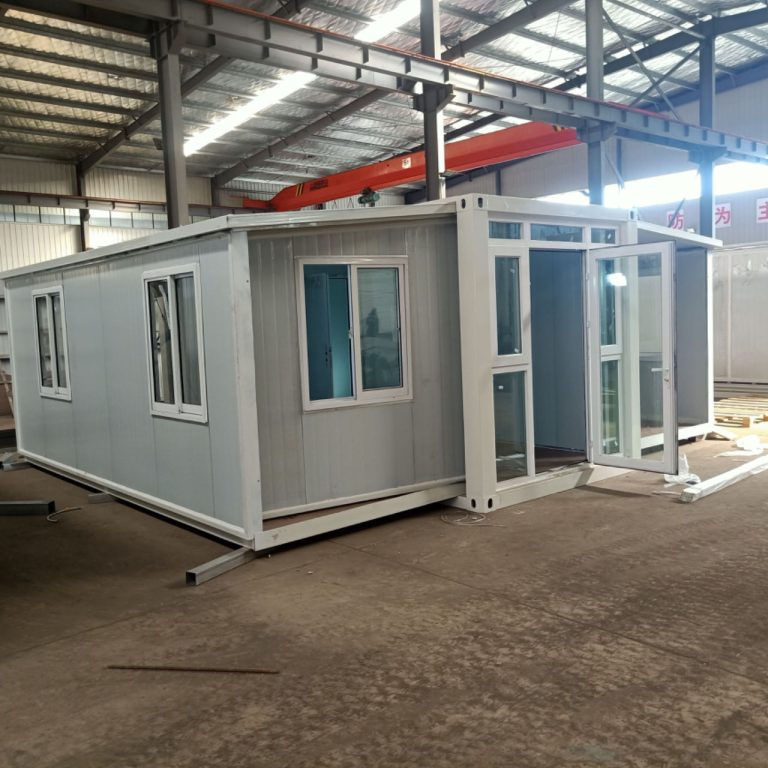
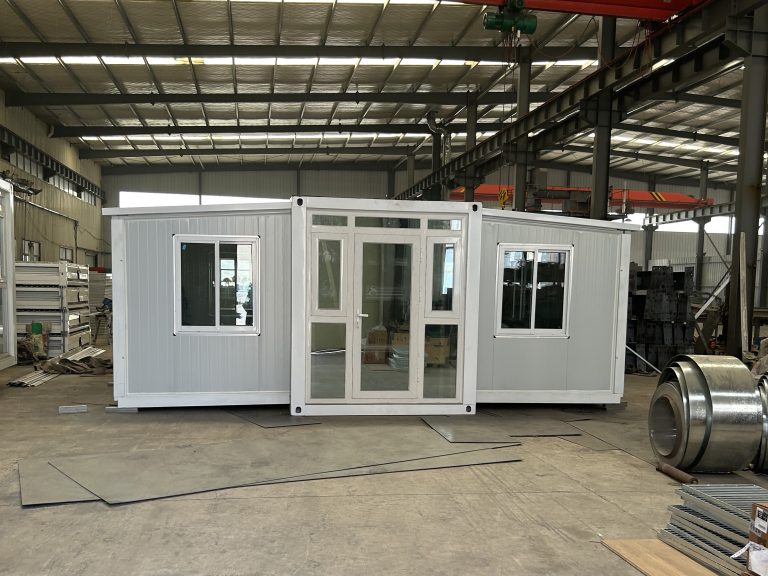
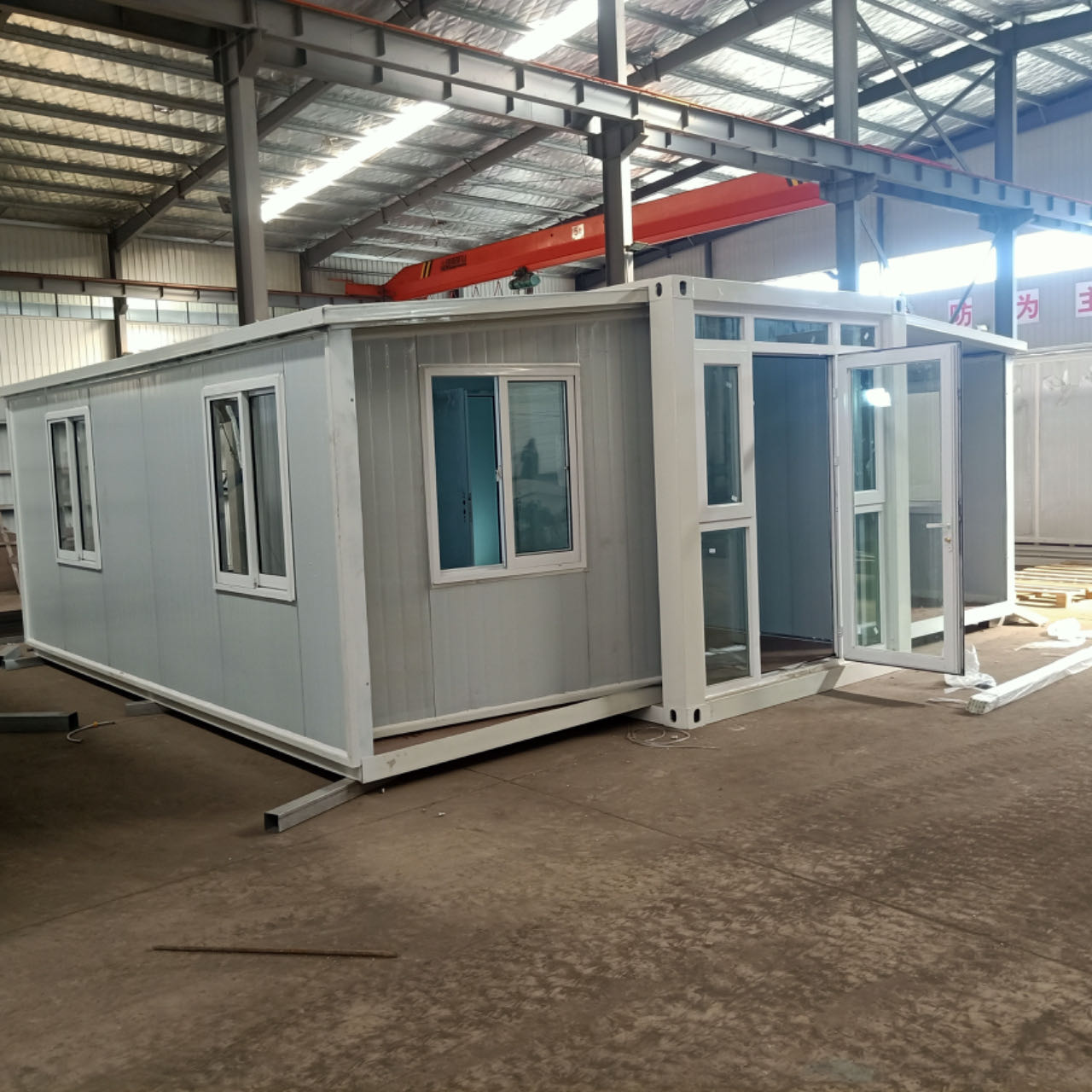
The increasing emphasis on sustainable construction practices has led to a growing interest in innovative building solutions, among which steel structure box houses stand out for their numerous benefits in green building evaluation systems. These structures, characterized by their modular design and efficient use of materials, offer a compelling alternative to traditional building methods, aligning closely with the principles of sustainability and environmental responsibility. One of the primary advantages of steel structure box houses is their inherent durability. Steel, as a material, is resistant to many of the common issues that plague conventional building materials, such as rot, pests, and extreme weather conditions. This longevity not only reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements but also minimizes waste, contributing positively to the overall lifecycle assessment of the building.
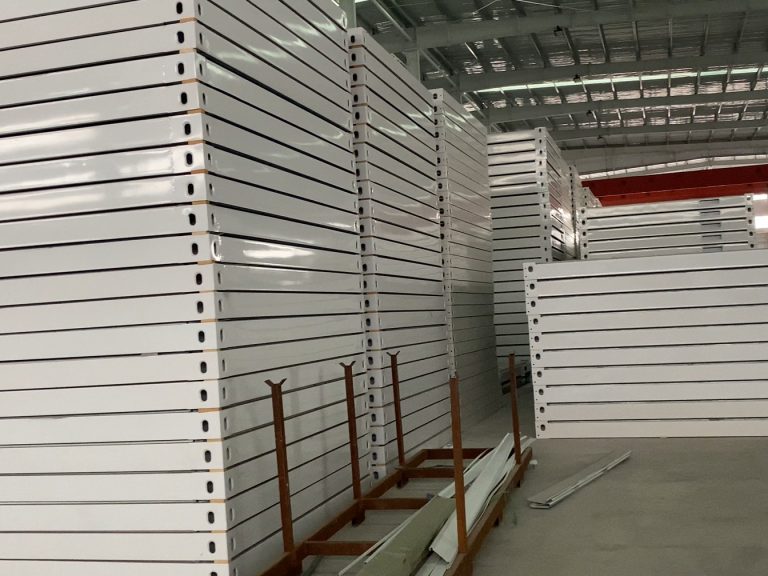
Moreover, the modular nature of steel structure box houses allows for significant reductions in construction time and labor costs. By utilizing prefabricated components, these structures can be assembled quickly on-site, which not only accelerates the building process but also reduces the environmental impact associated with prolonged construction activities. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in urban settings where time and space are at a premium. Additionally, the reduced construction time translates into lower energy consumption during the building phase, further enhancing the sustainability profile of steel structure box houses.

In terms of energy efficiency, steel structure box houses can be designed to incorporate advanced insulation materials and energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems. These features not only contribute to lower operational energy costs but also align with the criteria set forth by various green building evaluation systems, such as LEED and BREEAM. By achieving high energy performance ratings, these structures can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious builders and homeowners alike.
Furthermore, the recyclability of steel is a critical factor in the sustainability equation. Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, and its use in construction supports a circular economy. When a steel structure box house reaches the end of its life cycle, the steel components can be reclaimed and repurposed, thereby reducing the demand for new raw materials and minimizing landfill waste. This aspect not only enhances the environmental credentials of steel structure box houses but also resonates with the growing consumer preference for sustainable building practices.
Another noteworthy benefit is the flexibility and adaptability of steel structure box houses. Their modular design allows for easy reconfiguration and expansion, accommodating changing needs over time without significant structural alterations. This adaptability is particularly relevant in a world where demographic shifts and lifestyle changes are common, as it enables homeowners to modify their living spaces in response to evolving requirements. Consequently, this flexibility contributes to the long-term sustainability of the building, as it reduces the likelihood of obsolescence.
In conclusion, the benefits of steel structure box houses in green building evaluation systems are multifaceted, encompassing durability, energy efficiency, recyclability, and adaptability. As the construction industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable practices, these structures present a viable solution that not only meets the demands of modern living but also aligns with the principles of environmental stewardship. By integrating steel structure box houses into green building initiatives, stakeholders can significantly enhance their sustainability outcomes, paving the way for a more responsible and resilient built environment.
Challenges and Opportunities for Steel Structure Box Houses in Green Building Evaluation Systems
The emergence of steel structure box houses represents a significant innovation in the realm of sustainable architecture, particularly within the context of green building evaluation systems. However, while these structures offer numerous advantages, they also face a variety of challenges that must be addressed to fully realize their potential. One of the primary challenges is the perception of steel as a material that is not inherently sustainable. Critics often point to the energy-intensive processes involved in steel production, which can result in substantial carbon emissions. This perception can hinder the acceptance of steel structure box houses within green building evaluation frameworks that prioritize low-impact materials. Nevertheless, advancements in steel production, such as the development of recycled steel and the use of renewable energy sources in manufacturing, are beginning to mitigate these concerns. By emphasizing these innovations, proponents of steel structure box houses can better align their designs with the principles of sustainability.
In addition to material concerns, the design and construction processes associated with steel structure box houses present both challenges and opportunities. The modular nature of these structures allows for rapid assembly and reduced construction waste, which are significant advantages in the context of green building. However, the initial costs associated with steel construction can be higher than traditional building methods, which may deter some developers. To overcome this barrier, it is essential to highlight the long-term benefits of steel structure box houses, including durability, low maintenance requirements, and energy efficiency. By demonstrating the lifecycle cost advantages, stakeholders can make a compelling case for the adoption of steel structures in green building projects.
Moreover, the integration of steel structure box houses into existing green building evaluation systems poses another challenge. Many of these systems, such as LEED or BREEAM, have established criteria that may not fully account for the unique characteristics of steel construction. This misalignment can lead to difficulties in achieving certification, which is often a critical factor for developers. To address this issue, it is crucial for industry professionals to engage with green building organizations to advocate for the inclusion of steel structure box houses in evaluation criteria. By collaborating with these organizations, stakeholders can help shape the future of green building standards to better reflect the benefits of innovative construction methods.
On the other hand, the growing emphasis on sustainability in the construction industry presents a significant opportunity for steel structure box houses. As more consumers and businesses prioritize environmentally friendly building practices, the demand for sustainable housing solutions is likely to increase. This shift in market dynamics can create a favorable environment for steel structure box houses, particularly if they are marketed effectively as a viable alternative to traditional building methods. Furthermore, the potential for integrating renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and green roofs, into steel structure box houses enhances their appeal within green building evaluation systems. By showcasing these features, developers can position their projects as leaders in sustainable design.
In conclusion, while steel structure box houses face challenges related to material perception, cost, and integration into green building evaluation systems, they also present significant opportunities for innovation and sustainability. By addressing these challenges through advocacy, education, and strategic marketing, stakeholders can enhance the acceptance and viability of steel structure box houses in the green building sector. As the industry continues to evolve, the potential for these structures to contribute meaningfully to sustainable development remains promising, paving the way for a more environmentally conscious future in construction.